Phosphorus Discovered on Saturn's Moon Enceladus Makes It The Perfect Saucepan To Harbor Life

NASA's digital Europa Clipper poster is available at: https://europa.nasa.gov/resources/173/europa-clipper-journey-to-an-ocean-world-poster/Image credit: NASA/ Jet Propulsion Laboratory-Caltech.
In a remarkable breakthrough, scientists have detected the presence of phosphorus on Saturn's moon Enceladus, offering new and intriguing insights into the moon's potential for hosting life. The discovery was made through data collected by NASA's Cassini spacecraft during its close flybys of Enceladus, providing compelling evidence of the moon's complex chemistry and habitability.
Enceladus has long captivated researchers due to its subsurface ocean, believed to exist beneath its icy crust. This global ocean, kept in a liquid state by the moon's tidal interactions with Saturn, has made Enceladus an enticing target for the search for extraterrestrial life. Previous findings from Cassini have revealed the presence of water vapor, organic molecules, and hydrothermal activity within the moon's plumes, further fueling scientific curiosity.
Now, the detection of phosphorus on Enceladus adds another crucial piece to the puzzle. Phosphorus is an essential element for life as we know it, playing a fundamental role in the structure of DNA, RNA, and cell membranes. Its presence on Enceladus suggests the potential for the moon to harbor the building blocks necessary for life's emergence or sustenance.
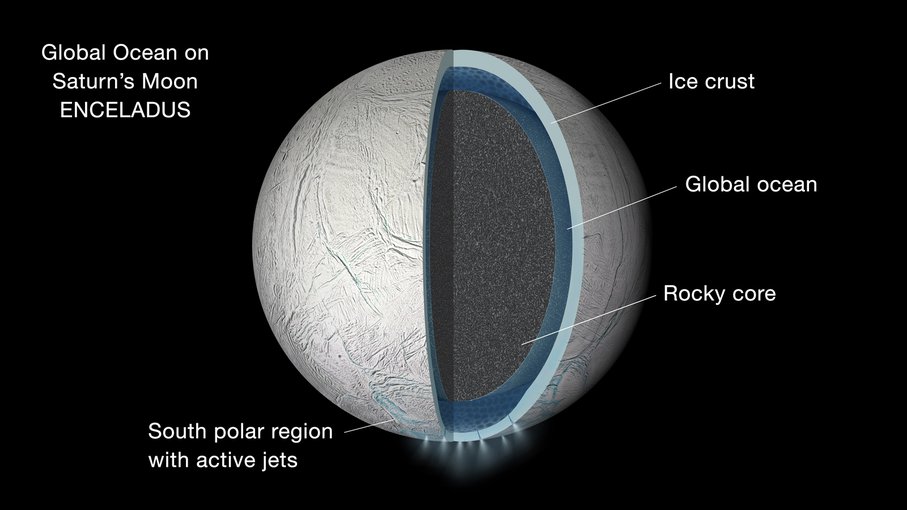
An artist depiction of the interior structure of Saturn’s moon Enceladus, showing an ocean trapped between an icy ceiling and a rocky bed at the ocean floor.Image credit: NASA/JPL–Caltech.
The Cassini spacecraft's Ion and Neutral Mass Spectrometer (INMS) was instrumental in making this discovery. By analyzing the composition of the plumes emitted from Enceladus, the INMS detected the distinctive signature of phosphorus, providing strong evidence for its existence on the moon's surface.
This finding raises fascinating questions about the origins and potential evolution of life beyond Earth. Enceladus' subsurface ocean, coupled with the presence of key ingredients such as water, organic molecules, and now phosphorus, offers a promising environment for the development of microbial life or even more complex organisms. The hydrothermal activity observed on Enceladus further enhances its potential as a habitable world.
The discovery of phosphorus on Enceladus underscores the importance of future exploration and in-depth study of this captivating moon. Upcoming missions and technological advancements will allow scientists to delve deeper into the moon's intriguing chemistry, with the aim of understanding its habitability and the potential for life.
NASA and other space agencies are already planning future missions that will focus on Enceladus, aiming to study its plumes and subsurface ocean more comprehensively. These missions will employ advanced instruments capable of characterizing the complex composition of Enceladus' geysers and further elucidating the moon's potential for hosting life.
As our understanding of Enceladus continues to evolve, it fuels our curiosity about the existence of life beyond our planet. The exploration of this enigmatic moon brings us closer to answering fundamental questions about the origins of life and the prevalence of habitable environments in the vastness of space.
The discovery of phosphorus on Enceladus serves as a testament to the remarkable scientific achievements and the ongoing quest for knowledge in our exploration of the cosmos. Each new revelation brings us one step closer to unlocking the mysteries of our universe and unraveling the potential for life beyond Earth.
Comments
Post a Comment